3.3.5
Discuss about Brush-less Motor
•
The mechanical "rotating
switch" or commutator/brushgear assembly is replaced by an external
electronic switch synchronised to the rotor's position.
•
Brushless motors are typically 85–90%
efficient or more, efficiency for a brushless electric motor.
•
Midway
between ordinary DC motors and stepper motors lies the realm of the brushless
DC motor.
•
Built very similar to stepper motors,
these often use a permanent magnet external rotor, three phases of driving
coils
•
Sensors
to sense the position of the rotor, and associated drive electronics.
•
Used where precise speed control is
necessary, as in computer disk drives or in video cassette recorders, the
spindles within CD, CD-ROM (etc.) drives, and mechanisms within office products
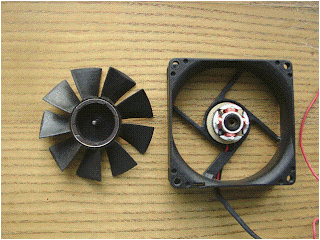
such as fans, laser printers and photocopiers.
VIDEO: How Brushless Motor Works!
Several
advantages over conventional motors:
•
Much cooler than
the equivalent AC motors.
•
Without a commutator to wear out,
the life of a DC brushless motor can be significantly longer compared
to a DC motor using brushes and a commutator.
•
Commutation also tends to cause a great
deal of electrical and RF noise; without a commutator or brushes, a brushless
motor may be used in electrically sensitive devices like audio equipment or
computers.
•
The same Hall effect sensors that
provide the commutation can also provide a convenient tachometer signal for
closed-loop control (servo-controlled) applications. In fans, the
tachometer signal can be used to derive a "fan OK" signal as well as
provide running speed feedback.
•
The motor can be easily synchronized to
an internal or external clock, leading to precise speed control.
•
Brushless motors have no chance of
sparking, unlike brushed motors, making them better suited to environments
with volatile chemicals and fuels. Also, sparking generates ozone which can
accumulate in poorly ventilated buildings risking harm to occupants' health.
•
Brushless motors are usually used in
small equipment such as computers and are generally used in fans to get rid of
unwanted heat.
•
They are also acoustically very quiet
motors which is an advantage if being used in equipment that is affected by
vibrations.
•
Modern DC brushless motors range in
power from a fraction of a watt to many kilowatts. Larger brushless motors
up to about 100 kW rating are used in electric vehicles. They also find significant
use in high-performance electric model aircraft.
Figures: Fans in computer usually uses brushless dc motors
(Lost your Way? Use The 'CHAPTERS TAB'!!)

No comments:
Post a Comment